|
Structural basis for
sequence-dependent DNA cleavage by nonspecific
endonucleases Yi-TingWang1,2,
Wei-Jen Yang1, Chia-Lung Li1, Lyudmila G. Doudeva1 and
Hanna S. Yuan1,* 1 Institute of Molecular Biology, Academia Sinica, 2 Institute of Biochemistry, ABSTRACT Nonspecific endonucleases hydrolyze
DNA without sequence specificity but with sequence preference,however the structural
basis for cleavage preference remains elusive. We show here that the
nonspecific endonuclease ColE7 cleaves DNA with a preference for making nicks
after (at 30O-side) thymine bases but the periplasmic nuclease Vvn cleaves DNA
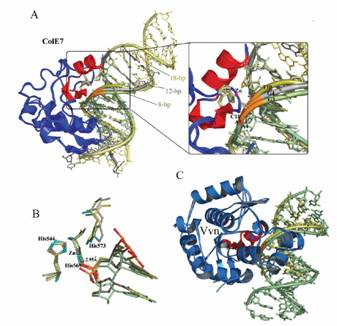
more evenly with little sequence preference. The crystal structure of the
‘preferred complex’ of the nuclease domain of ColE7 bound to an 18 bp DNA
with a thymine before the scissile phosphate had a more distorted DNA
phosphate backbone than the backbones in the non-preferred complexes, so that
the scissile phosphate was compositionally closer to the endonuclease active
site resulting in more efficient DNA cleavage. On the other hand, in the
crystal structure of Vvn in complex with a 16 bp DNA, the DNA phosphate
backbone was similar and not distorted in comparison with that of a
previously reported complex of Vvn with a different DNA sequence. Taken
together these results suggest a general structural basis for the
sequencedependent DNA cleavage catalyzed by nonspecific endonucleases,
indicating that nonspecific nucleases could induce DNA to deform to
distinctivelevels depending on the local sequence leading todifferent
cleavage rates along the DNA chain.
|
|
Reprint file: (pdf) |