| The preliminary crystallographic analysis
of the open-form E. coli tyrosine aminotransferase bound with a
cofactor pyridoxal 5-phosphate
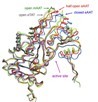
Ko, T. P., Yang, W.-Z, Wu, S.-P., Hsin, T., and Yuan, H. S. Abstract Tyrosine aminotransferase catalyzes the transamination for both dicarboxylic and aromatic amino acid substrates. The substrate-free Escherichia coli tyrosine aminotransferase (eTAT) bound with a cofactor pyridoxal 5-phosphate (PLP) was crystallized in trigonal space group P32. A low resolution crystal structure of eTAT was determined by molecular replacement methods. The overall folding of eTAT resembles those of aspartate aminotransferases with two identical subunits forming a dimer in which each monomer binds a PLP molecule via a covalent bond linked to the e-NH2 group of Lys258. Comparison of the structure of eTAT with those of open, half-open or closed form of chicken or E. coli aspartate aminotransferases shows that the eTAT structure is in the open conformation. |